Discover the root cause of your gum problems, then learn how to treat severe periodontal disease.
Periodontitis treatment is essential to eradicate bacteria from the oral cavity and it is done to simulate the healing of the affected area, or areas in most cases. If you have gingivitis, periodontitis or ANUG (Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis), you are not alone. There are many people who have the same problem. Therefore, do not lose hope, as the infection can be resolved, with the proper dental techniques, of course. However, please remember that your infection should not be taken lightly. In some cases, severe forms of periodontal disease can affect your system, as the bacteria may travel to other parts of the body.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of periodontal gum disease. The progress of periodontal disease is generally broken down into two phases. it is very important to understand that you do not simply wake up one day and immediately have it. There is a disease of the gums that has been progressing up to this point. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the progression of gum disease and its root cause.
So in summary, periodontitis is severe, advanced gum disease.
What is the Cause of Periodontal Disease?
Before we discuss periodontal treatments, it is important to tackle the reasons why people have gum problems. There are a lot of factors that can lead to this condition. However, the main reason is that the normal amount of bacteria has multiplied. This may be caused by plaque, tartar, being immune-compromised, hormonal changes or certain medications for hypertension and seizures.
Since the mouth contains 500 or more species of microorganisms regularly, it is important to maintain proper oral hygiene. This will keep the levels of bacteria to a minimum. Microorganisms multiply in number when there are large amounts of plaque or tartar deposits. Food debris provides these organisms with ample nutrients needed to multiply in number. When the volume of bacteria is greater than normal, infection will begin.
Once this happens, our immune system goes on overdrive. It releases chemicals to combat the bacteria. Macrophages play an important role in this case. They engulf the bacteria and cover them with chemicals. This makes it easier for our other cells to destroy the organisms. However, the chemicals produced during this process will harm the tissues in the affected area. This causes inflammation.
Discover a formula that combats the root cause of periodontitis.
Stages of Periodontal Disease
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease. It is characterized by red, inflamed and painful gums. Bleeding occurs during brushing and even with slight contact. This is a reversible condition that can be done with the help of proper brushing and flossing techniques. It is best to go to your dentist once a month for thorough cleaning procedures.
No bone or tissue loss occurs during this stage. This means that if the problem is addressed during this phase, you will not have to worry about permanent damage. However, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible as the longer tartar and plaque stay on your teeth, the more harmful they can be.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis goes untreated, the damage becomes irreversible. A advanced conditions develops wherein the bacteria gains access to the bone and roots. The organisms invade the space between the roots and the alveolar socket. During this period, periodontal pockets are formed, as the gums and the tooth are separated by these areas filled with bacteria. The immune system will have to fight harder, as the infection begins to break down the structure of the root and the bone. If this is left untreated, there is a chance that the pocket may widen. The infection may spread to the soft tissue and the jaw.
Please note that teeth may become loosened, and they may have to be extracted. Please note that aside from the mentioned risk factors, smokers are at an increased risk of developing this problem. People who smoke and receive treatment may also expect a slimmer chance of success.
As mentioned above there may be underlying contributing factors to aggressive and chronic periodontitis, such as a compromised immune system. Check with your medical doctor to discuss how underlying health conditions may be driving or contributing to the difficulty in controlling bacteria, thus the process of gum disease.
Stages of Gum Disease 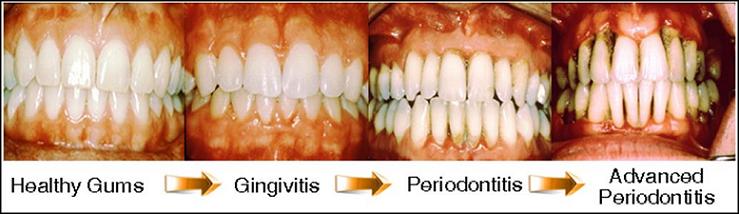
Signs of Advanced Periodontal Disease
During regular visits, your dentist will check your gums and teeth any distinguishing signs that the bacteria has set in:
- Receding gums
- Chronic bad breath
- Gum inflammation
- swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Loose teeth
- Gum abscess or pus
- Unaligned teeth
- Change in the depth of gum pockets.
Probing for Periodontal Pockets.
Once your periodontist or hygienist identifies the signs of gum disease or as part of the routine checkup, they may use a tiny probe, which resembles a ruler, to check the gumline for the presence of periodontal pockets. The normal probe depth should range between one to three millimeters. Anything deeper than that signifies the presence of a periodontal pocket. While this procedure is usually painless, people with periodontal pockets may feel slight to moderate discomfort, owing to the infection. Many dentists use an electronic probe that records the depth at each visit.
X-Rays to Reveal Bone Deterioration.
The dentist may also take an x-ray to confirm the presence of gum disease. If pockets are present, he or she will refer you to a periodontist, as this specialist will have the expertise necessary to treat the condition.
Give More Attention When You have a Chronic Illness.
However, if you have any systemic illness or are taking medication that can cause gum problems, you may be asked to visit every one to two months as a precautionary measure.
Periodontitis Treatment
The periodontist’s main goal will be to control the spread of infection. The treatment will usually require multiple visits. The number will vary, based on the extent of the damage. However, please note that it is important to practice proper oral hygiene techniques at home as well. Please note that smokers may be asked to quit, as smoking will lessen the effectiveness of the treatment.
Scaling and Root Planing
This technique is done to remove the plaque above and under the gumline. Scaling is the process wherein scraping is done to remove tartar. Root planing technique that makes use of a tool to smoothen out rough spots on the roots. These areas are infected with microorganisms that cause the disease. Please note that the dentist may use manual tools or a laser to achieve the desired result.
Medicine
Medication is needed to resolve the problem. Chlorhexidine mouthwash may be prescribed for home care. This formula controls bacteria and is used just like regular mouthwash. You may be asked to switch to a liquid toothpaste. Most periodontists prefer them, as the regular dentifrice has harsh ingredients that may damage the sensitive area. He or she will usually prescribe a natural cleaning solution that contains essential oils with antimicrobial properties.
An antiseptic chip may be inserted into the area. It will contain chlorhexidine and be placed in the periodontal pocket to reduce the infection. Anti-bacterial gel may also be placed in the periodontal space. Lastly, oral antibiotics are usually prescribed to control the infection. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will also be given, to lessen the discomfort and inflammation cause by the invasive treatment.
Flap Surgery
In cases wherein an extensive area is involved; flap surgery may be required. This is done when the pockets are very deep. This technique is required to remove tartar deposits found in deeper pockets. The gum area is incised and lifted away for the procedure. Once the plaque and tartar have been removed, the gingiva is sutured back. Patients will notice that the gums will fit more tightly around the teeth after this procedure.
Gum Grafts
Gum grafts are performed by taking soft tissue from other areas of the mouth and transferring them to the cleaned area where there is a receding gum line. The tissue is sown to the affected area with hopes that they will cover gums that have receded. It can be a painful and costly procedure. There are newer procedures available, such as the Pinhole Surgical Technique™ that are less radical and offer a quicker recovery time, but can also be costly.
Tissue And Bone Graft Techniques
A graft may be required for severe cases wherein there is bone loss. Synthetic bone is placed in the area to stimulate bone growth. Tissue grafts may also be required to cover any exposed roots. Synthetic material may be used. However, in most cases, tissue is harvested from another part of the oral cavity.
Periodontal Treatment Costs
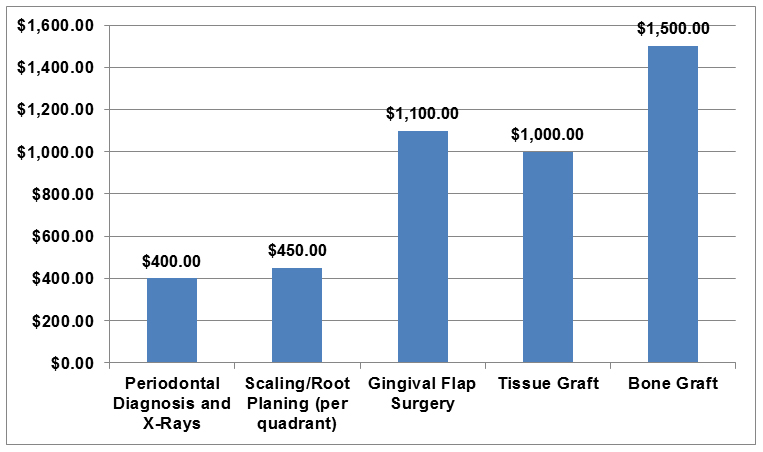
Your periodontist will choose a gum disease treatment according to your particular needs. Therefore, people with mild to moderate cases may not need to undergo flap surgery or grafts as those procedures. However, please note that each treatment comes with a possible percentage of failure, depending on your case and how well you follow the post-operative care procedures at home. Everyone, however, must deal with the root cause of gum disease – bacteria. Kill it or it may kill you, literally!
If you are looking for a periodontitis cure, natural options may not reverse the damage already done. However, together with the help of your periodontist, a natural periodontitis treatment solution may effectively kill and subdue the root cause — uncontrolled bacteria. This is a non-negotiable. What are you waiting for?